Wind energy comes from harnessing the power of wind to generate electricity. It is a renewable source of energy that has gained popularity due to its environmental benefits and ability to reduce dependency on fossil fuels.
Wind energy is derived from the wind’s kinetic energy, which is converted into mechanical energy by wind turbines. These turbines consist of large blades that rotate when the wind blows. The rotation of the blades spins a generator, producing electricity.
Wind energy is abundant and can be harnessed in various locations, including onshore and offshore wind farms. It is a clean and sustainable energy source that helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigates climate change. As a result, wind energy has become an essential part of the global transition to a greener and more sustainable future.

Credit: slideplayer.com
The Origins Of Wind Energy
Wind energy has a long history that stretches back thousands of years. Since ancient times, humans have been harnessing the power of the wind for various purposes. In this section, we will delve into the origins of wind energy, exploring how it has been harnessed and utilized throughout history.
Harnessing The Power Of The Wind
Humans have been harnessing the power of the wind for centuries, recognizing its potential as a valuable energy source. The concept of harnessing wind energy revolves around converting the kinetic energy of the wind into mechanical or electrical energy that can be used to power different devices or utilities.
One of the most common ways to harness wind energy is through wind turbines. These large structures consist of rotor blades attached to a central hub, which transforms the wind’s energy into rotational motion. The spinning motion of the rotor blades activates a generator within the turbine, producing electricity that can be utilized for various purposes.
Historical Use Of Wind Energy
The historical use of wind energy dates back to ancient times. The earliest evidence of windmills can be traced back to around 2000 BC, when they were used in Persia (modern-day Iran) for grinding grain and pumping water. These early windmills featured vertical-axis designs and were commonly used in regions with strong prevailing winds.
As civilizations advanced, wind energy continued to play an essential role in various industries. In the 12th century, the horizontal-axis windmill, similar to the ones we see today, was developed in Europe. These windmills were not only used for grinding grain but also for sawing wood, processing textiles, and even pumping water.
Throughout history, wind energy has been vital to maritime activities. Sailboats and ships relied on the wind’s power to navigate the vast seas, making wind energy instrumental in trade and exploration. Wind propulsion also played a key role in the development of windmills, as the mechanism used in sailboats was adapted to harness wind power on land.
Fast forward to the modern era, and wind energy has become increasingly popular as a renewable energy source. Wind farms with multiple wind turbines have popped up worldwide, generating clean electricity for communities and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
In conclusion, the origins of wind energy can be traced back thousands of years. From ancient windmills used for grinding grain to modern wind turbines powering entire communities, humans have long recognized the potential of wind as a valuable energy source.
The history of wind energy serves as a testament to our continuous efforts to harness and utilize renewable energy for a sustainable future.
How Wind Energy Is Generated
Wind energy is a renewable and sustainable source of power that has been harnessed for centuries to generate electricity. It is a clean and eco-friendly alternative to traditional fossil fuels, making it a popular choice in the pursuit of greener energy. Understanding how wind energy is generated sheds light on the technology and infrastructure behind this clean power source.
Wind Turbines: An Overview
The backbone of wind energy generation is the ubiquitous wind turbine. These tall, sleek structures are typically made up of a tower, rotor blades, nacelle, and other intricate components. Wind turbines are strategically placed in areas where there is a consistent and strong flow of wind, allowing for maximum energy capture.
The Inner Workings Of A Wind Turbine
Within the nacelle of the wind turbine, a gearbox and generator work in symbiosis to convert the kinetic energy from the rotating blades into electrical power. The rotor blades are designed to capture the kinetic energy of the wind, causing them to spin, which in turn drives the shaft connected to the gearbox. The gearbox then amplifies the rotational speed, transferring it to the generator where it is converted into usable electricity.
Advantages Of Wind Energy
Wind energy is a form of renewable energy that is harnessed from the power of wind. This clean and abundant source of energy has gained popularity in recent years as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. Harnessing the power of wind can have numerous advantages, making wind energy an attractive option for generating electricity.
Renewable And Sustainable
The main advantage of wind energy is that it is renewable and sustainable. Unlike fossil fuels such as coal and natural gas, which are finite resources that will eventually run out, wind energy is inexhaustible. As long as the wind blows, we can continue to harness its power to generate electricity. This sustainability ensures a stable and reliable source of energy for future generations.
Reduces Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Wind energy also offers an important environmental advantage by significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Unlike traditional power plants that rely on fossil fuels, wind turbines produce electricity without burning any fuel. This means that wind energy production does not release harmful pollutants such as carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, or nitrogen oxide, which contribute to climate change and air pollution. By replacing fossil fuel-based electricity generation with wind energy, we can mitigate the impacts of global warming and improve air quality.
Challenges And Limitations In Wind Energy
Intermittency and Grid Integration
Wind energy, although a promising renewable energy source, faces certain challenges and limitations. One significant obstacle is the intermittency of wind power generation. Wind is not a constant resource and can vary in speed and consistency. This fluctuation creates challenges in integrating wind energy into the power grid.
Intermittency: The intermittency of wind energy refers to the variability in wind speed and direction. While ideal wind conditions can lead to optimal power generation, the absence or inconsistency of wind poses a significant challenge. This unpredictability can cause fluctuations in grid stability and impact the reliability of power supply.
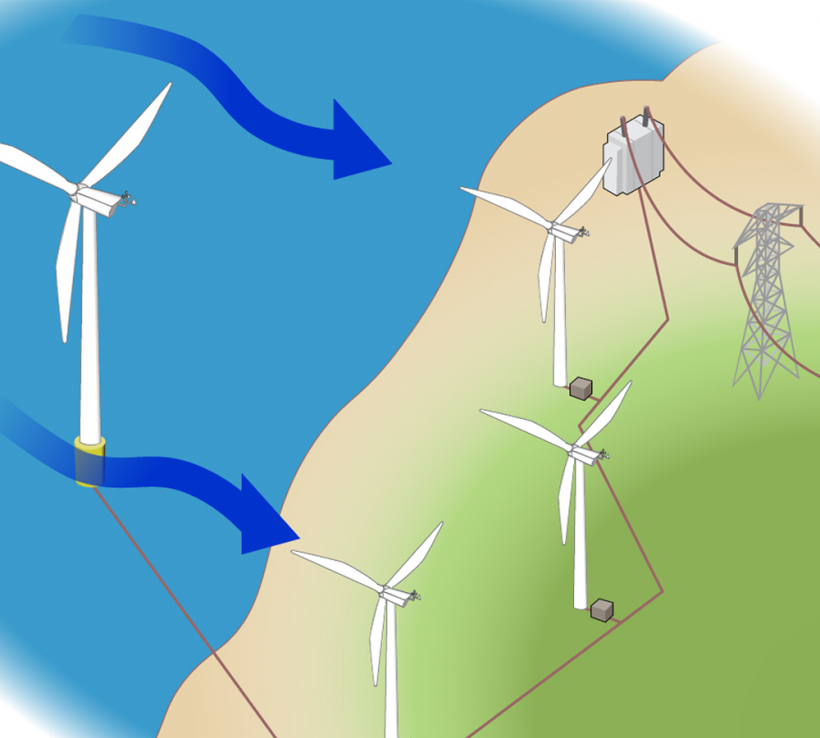
Grid Integration: Integrating wind energy into the power grid necessitates careful planning and management. The power grid must be capable of accommodating the intermittent nature of wind generation. Additionally, wind farms are often located in remote areas, far from heavily populated regions where electricity demand is highest. As a result, the power generated must be transmitted efficiently over long distances, which can be challenging and expensive.
To address these challenges, innovative solutions are being pursued. One approach is the development of advanced energy storage technologies. By implementing large-scale energy storage systems, excess wind power can be stored during periods of high generation and released during periods of low generation, thus mitigating the impact of intermittency and enabling better grid integration.
Environmental Considerations
Wind energy is generally considered environmentally friendly; however, there are certain considerations to be aware of:
| Environmental Considerations | Description |
|---|---|
| Visual impact | Wind turbines can be visible from long distances, leading to aesthetic concerns and possible opposition. |
| Flight patterns and wildlife | Wind turbines can interfere with bird migration patterns and pose risks to avian species. |
| Noise pollution | Wind turbines can generate noise, which can be bothersome for communities living in close proximity to wind farms. |
| Land and habitat disruption | Building wind farms requires extensive land use, potentially resulting in the displacement of local flora and fauna. |
Despite these considerations, wind energy remains one of the most sustainable and cleaner energy options available. Continued research and advancements in technology will help address these environmental concerns while maximizing the benefits of wind power.
The Future Of Wind Energy
Wind energy holds immense potential as a sustainable and eco-friendly source of power and is expected to play a vital role in the future of energy production. The industry is witnessing exciting advancements in technology and integration with other renewable energy sources, paving the way for increased efficiency and widespread adoption.
Technological Innovations
Advancements in wind turbine technology are continuously driving the future of wind energy. Innovations such as larger rotor diameters, taller towers, and improved blade designs are boosting energy capture and making wind power more cost-effective. Additionally, the development of smart control systems and predictive maintenance technology is enhancing the performance and longevity of wind turbines.
Integration With Other Renewable Energy Sources
- Wind energy is being increasingly integrated with other renewable sources such as solar power and energy storage systems, creating hybrid energy solutions that offer a more reliable and consistent supply of electricity.
- The complementary nature of wind and solar power allows for enhanced grid stability by balancing out fluctuations in energy production, contributing to a more resilient and sustainable energy infrastructure.

Credit: www.inspirecleanenergy.com

Credit: www.eia.gov
Conclusion
Wind energy is a valuable renewable resource that comes from the natural movement of air. Harnessing this power through wind turbines has proven to be an efficient and sustainable way to generate electricity. As we continue to explore green energy alternatives, wind energy will play a significant role in reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and combating climate change.